When you hear the term emotional dysregulation test, it’s easy to picture a single, formal exam. In reality, it’s not one specific test but a thorough assessment process clinicians use to get a clear picture of how someone experiences and manages their feelings. It's a crucial tool, particularly for identifying underlying conditions like ADHD and autism, where intense emotional responses are often part of the daily experience and deeply impact mental health.
What Is an Emotional Dysregulation Test and Why Is It Important for Mental Health?

Think of your emotions like the volume dial on a stereo. For most people, it turns smoothly, allowing for precise control. For someone with emotional dysregulation, that dial is incredibly sensitive. A small trigger can crank the volume to maximum in an instant, and turning it back down feels like a slow, difficult struggle.
That’s the essence of emotional dysregulation: feeling emotions more intensely, and for longer, than the situation seems to call for. This can turn everyday frustrations into overwhelming crises that take a significant toll on one's mental health.
The Role of an Assessment
An emotional dysregulation test is designed to measure how sensitive that internal volume dial is. It’s never about judging your feelings as "right" or "wrong." Instead, it provides a clear, objective look at your emotional patterns, which is especially vital for adults and children who suspect they might be neurodivergent.
An assessment acts as a roadmap, translating confusing emotional experiences into understandable patterns. It helps pinpoint why you react the way you do, moving you from self-blame towards effective solutions and self-compassion.
This process is so important because emotional dysregulation is a key, yet often overlooked, feature of several mental health conditions. Recognising these patterns is the first step towards an accurate diagnosis and, more importantly, finding support that actually works.
Its Connection to ADHD, Autism, and Mental Health
While many people associate ADHD strictly with focus or hyperactivity, intense emotional reactions are a fundamental part of the experience for a huge number of individuals. Likewise, for autistic people, sensory overload or communication challenges can trigger emotional responses that might seem disproportionate from the outside but make perfect sense within their internal world.
This is why a proper assessment is such a game-changer. It helps a clinician differentiate between various conditions and ensures you get support tailored to your unique brain and mental health needs.
It's not just about ADHD and autism, either. Emotional dysregulation is a significant challenge in other mental health conditions too. For instance, understanding its role in cases of comorbid Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) highlights why a skilled emotional assessment is vital across the entire mental health spectrum.
A professionally guided evaluation can untangle these connections. If you're wondering what to do next, a comprehensive mental health assessment online can bring much-needed clarity to your emotional world and help you find a path forward.
The Unseen Link Between ADHD and Emotional Intensity

When we talk about ADHD, conversations often turn to focus, organisation, or restlessness. But for many adults, the toughest daily battles are fought internally, against powerful waves of emotion that can feel overwhelming and appear out of nowhere. This emotional dysregulation isn't just a side effect; it's now widely recognised as a core feature of ADHD that significantly impacts mental health, though it remains one of the most misunderstood aspects of the condition.
Think of it like driving a high-performance sports car. The engine is incredibly powerful, and your emotions accelerate with breathtaking speed and force. The problem? The brakes feel sluggish and unresponsive. Trying to slow down, change gear, or simply cruise at a steady pace feels next to impossible. This analogy gets to the heart of emotional intensity in ADHD – the reactions aren't just bigger, they're faster and far harder to manage.
This isn't just a feeling; it's a reality backed by solid clinical evidence. Study after study confirms that people with ADHD tend to experience emotions more intensely and have a much harder time regulating them compared to their neurotypical peers. It’s why a proper emotional dysregulation assessment can be a complete game-changer when it comes to getting an accurate ADHD diagnosis.
Rejection Sensitive Dysphoria
One of the most powerful and painful ways this emotional intensity shows up is through Rejection Sensitive Dysphoria (RSD). While it’s not an official diagnosis in itself, RSD is a term that perfectly describes an extreme sensitivity to being criticised or rejected – whether that rejection is real or just perceived.
For someone experiencing RSD, a throwaway comment or a simple misunderstanding can feel like a deep, personal wound, triggering an immediate and overwhelming emotional response. This isn't just a case of "being too sensitive." It's a genuine, all-consuming pain that can severely affect self-esteem and overall mental well-being. The fear of experiencing this pain often leads people into two distinct behavioural patterns:
- People-pleasing: Going to extraordinary lengths to be liked and approved of, all to avoid the slightest chance of disapproval.
- Avoidance: Completely pulling back from situations where rejection is a possibility. This can mean shying away from new friendships, job opportunities, or social events.
"For individuals with ADHD, the emotional brain can sometimes hijack the thinking brain. RSD is a powerful example of this, where the perception of rejection triggers a physical and emotional response that feels catastrophic and difficult to reason with."
Understanding RSD is vital because it shows how emotional dysregulation directly shapes a person's behaviour, self-worth, and major life choices. It really highlights why an emotional dysregulation test is so essential for seeing the full picture of someone's challenges. If this resonates with you, taking a look at other common ADHD symptoms in adults might offer more context and validation for what you're going through.
The Science Behind the Emotional Storm
The deep-seated link between ADHD and emotional dysregulation is rooted in our neurobiology. In the ADHD brain, key areas responsible for emotional control and executive functions – like the prefrontal cortex and the amygdala – operate differently. This can make it much more difficult to calm down the body's "fight or flight" response once it's been triggered.
This isn't just theory; it's a biological reality confirmed by significant UK-based research. A landmark study from the University of Cambridge, for instance, delved into the emotional lives of children with ADHD. The results were striking: 51.4% of children in the high-symptom group displayed clear signs of emotion dysregulation. This conclusion was drawn from detailed parent questionnaires about behaviours like being unable to control actions when upset or feeling intensely bad about themselves during emotional lows.
Crucially, the study identified this emotional component as a core part of ADHD, distinct from its more well-known cognitive challenges. You can read more about these research findings on emotion dysregulation in children. This evidence validates what countless individuals and their families have known for years. It confirms that the intense frustration over a tiny mistake or the explosive anger from a minor setback aren't character flaws—they are legitimate manifestations of ADHD's unique neurological wiring.
How Autism Shapes the Emotional Experience
While ADHD can feel like having an emotional accelerator that’s hard to control, emotional dysregulation in autism often comes from a completely different set of triggers. For autistic individuals, the entire emotional experience is shaped by a unique way of perceiving and interacting with the world, creating mental health challenges that demand a more specialised understanding.
Think about trying to have a quiet, meaningful conversation while every TV in a warehouse is blaring a different channel at full volume. That’s a pretty good analogy for how sensory input can feel for an autistic person. Sights, sounds, textures, and smells that most people filter out can become an overwhelming flood, leading to a state of sensory overload. When your nervous system is pushed that far, the ability to manage emotions simply plummets.
This sensory bombardment is often what leads to meltdowns or shutdowns. It's crucial to understand these aren't tantrums or choices; they are intense, involuntary responses to unbearable distress. A meltdown might look like crying, shouting, or physical agitation. A shutdown can look like the complete opposite—total withdrawal or becoming non-responsive. Both are signs that a person's system has been pushed far beyond its limits.
The Challenge of Naming Emotions
Adding another layer of complexity is a trait called alexithymia, which is very common in the autistic community. Alexithymia isn't an absence of feelings. It's a genuine difficulty in identifying, describing, and telling the difference between your own emotions. Imagine having a rich, complex inner world of feelings but being unable to find the right words to label or make sense of them.
This creates a huge barrier to self-regulation. If you can’t recognise that you’re feeling anxious until it’s already spiralled into panic, it’s almost impossible to use coping strategies in time. Any emotional dysregulation test for an autistic person has to take alexithymia into account, because a standard question like "How often do you feel sad?" might not get to the heart of their true emotional state. Understanding more about the internal world of autistic adults provides crucial context; you can explore this further in our detailed guide on what Autism Spectrum Disorder is in adults.
Communication Differences and Emotional Signals
The way autistic people communicate and read social cues also plays a massive part in emotional dysregulation. Constant misunderstandings can breed frustration and anxiety. On top of that, the effort of "masking"—consciously hiding natural autistic traits just to fit in—is mentally draining and leaves very little energy left for managing emotions.
For an autistic person, behaviours that others might label as aggression or withdrawal are often just desperate signals of profound internal distress. They become a form of communication when words fail or their internal system is completely overwhelmed. A good assessment looks past the behaviour to find its root cause.
A UK study on autistic adolescents showed this connection clearly. Researchers surveyed 398 caregivers and found that social communication difficulties were a direct pathway to aggressive behaviours. Why? Because these struggles fuelled intense emotional dysregulation. The study used a detailed emotional reactivity scale to show that when autistic teens couldn’t make sense of social situations, their emotional turmoil ramped up, which in turn led to these outward behaviours. You can discover more insights about how communication impacts emotional regulation in autistic youth in the full study.
This is exactly why a generic emotional dysregulation test often misses the mark for autistic individuals. To be genuinely helpful, an assessment needs to be built around the autistic experience, considering sensory profiles, communication styles, and the possibility of alexithymia to create a truly accurate and compassionate picture of someone's emotional world.
Decoding the Different Types of Emotional Assessments
When you start looking for answers about your emotional world, you’ll quickly find a confusing mix of options. From quick online quizzes to in-depth clinical evaluations, it’s hard to know which path is right for you. Understanding the difference is the first, most crucial step toward getting the clarity you need.
Let’s use an analogy. An online screener is like looking at your house on a satellite map. You get a general overview—its shape, its location—but not much detail. A formal clinical assessment, on the other hand, is like having a qualified surveyor walk through every room, check the foundations, and hand you a detailed blueprint. One offers a hint; the other provides a reliable, in-depth understanding.
The Role of Online Screeners and Quizzes
Free online quizzes are often an accessible starting point. They’ll typically ask about your reactions to stress, the intensity of your feelings, or how easily you can calm down. For many people, these screeners are the first time they see their private struggles reflected back at them, which can be incredibly validating.
But it’s vital to see them for what they are. An emotional dysregulation test you find online is not a diagnostic tool. It simply doesn't have the scientific rigour or clinical context required for an accurate diagnosis. Privacy can also be a major concern—you often have no idea who is collecting your personal data or how it’s being used.
These tools are great for self-reflection, but they can’t replace the expertise of a trained mental health professional. For those looking for a structured, yet preliminary, exploration from a trusted source, something like an online ADHD test can offer some initial direction before committing to a full evaluation.
What a Formal Clinical Assessment Involves
A professional assessment is a far more robust and detailed process. It isn't just a single questionnaire but a multi-faceted evaluation carried out by a qualified psychologist or psychiatrist. The goal is to build a complete picture of your emotional functioning, rule out other potential causes, and arrive at an accurate, helpful diagnosis.
To help illustrate the key differences, here’s a quick comparison of what you can expect from each approach.
Online Screener vs Clinical Assessment
| Feature | Online Screener | Formal Clinical Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Self-reflection and preliminary insight. | Diagnosis, treatment planning, and access to support. |
| Accuracy | Low to moderate; not scientifically validated for diagnosis. | High; uses evidence-based, standardised tools. |
| Conducted By | Automated algorithm (self-administered). | Qualified psychologist or psychiatrist. |
| Process | A brief set of questions, usually taking a few minutes. | Multi-faceted: clinical interviews, validated questionnaires, observation. |
| Outcome | An informal score or category suggesting potential traits. | A comprehensive diagnostic report with personalised recommendations. |
| Privacy | Often uncertain; data collection policies can be unclear. | Confidential and protected by strict clinical privacy laws. |
As the table shows, a formal assessment is a deep dive, not just a surface-level glance.
A comprehensive evaluation typically includes several key components:
- Structured Clinical Interviews: This is a guided conversation where a clinician asks detailed questions about your developmental history, emotional experiences, and daily challenges. It helps them understand your struggles within the full context of your life.
- Validated Questionnaires: Unlike informal quizzes, these are scientifically designed and tested tools. Good examples include the Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale (DERS), and in the UK, the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) is often used for children and adolescents.
- Observational Data: A skilled clinician also pays close attention to non-verbal cues and how you interact during the assessment. Sometimes, they may ask for input from a partner, parent, or teacher to get a broader, more rounded perspective.
The diagram below shows the kind of emotional pathway often seen in autism, where overload can progress to a meltdown and then withdrawal. A thorough clinical assessment is designed to uncover and understand these underlying patterns.
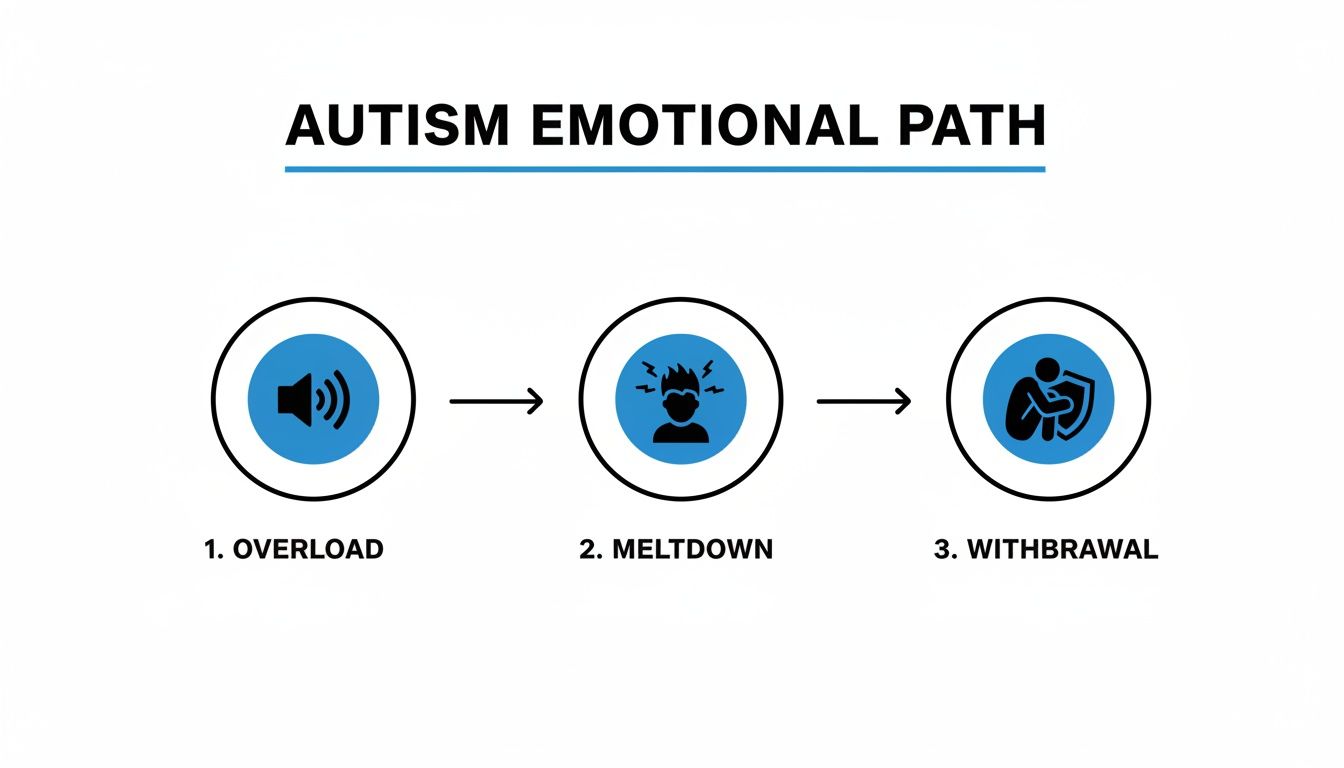
This process really highlights why behaviours like meltdowns aren't random. They are often the final, visible stage of an overwhelming internal experience that a formal assessment can help decode.
Why Standardised Tools Matter
Using standardised tools is crucial because they provide objective data that helps track emotional challenges consistently over time. The UK's Millennium Cohort Study offers a powerful real-world example.
In the study, the average score on the CSBQ Emotional Dysregulation scale for children at age 3 was 9.33, showing that significant challenges in managing feelings can be present from a very young age. By age 7, emotional symptoms measured by the SDQ had increased, revealing a clear developmental trend. You can learn more about these emotional development findings in children directly from the research.
A professional clinical assessment is the only reliable path to a formal diagnosis. It moves beyond self-reflection into the realm of evidence-based evaluation, providing the certainty needed to access the right support and build effective strategies for the future.
Ultimately, while an online screener might open the door to self-awareness, only a formal clinical assessment can give you the detailed blueprint needed to truly understand your emotional world and take confident next steps.
Turning Your Results Into Action

Getting the results from an emotional dysregulation test isn't the end of the road. In fact, it's the very beginning. This new information isn’t meant to be a label that defines you; think of it more like a lens, helping you see your own experiences with more clarity and compassion. It’s the first real step from feeling confused to feeling in control of your mental health.
Your assessment results are essentially a personalised map of your emotional world. The scores and clinical notes highlight the unique terrain you deal with every day—the steep climbs of high emotional reactivity, the hairpin turns of impulsivity, or the thick fog of not being able to name your feelings. Once you understand this map, you can start plotting a new, more manageable path forward.
A high score in emotional reactivity, for example, could finally explain why a small setback at work feels like a personal catastrophe. Likewise, recognising a pattern of poor impulse control can shed light on why certain relationships or spending habits have always felt so chaotic. These aren't personal failings; they're patterns that can be understood and addressed.
From Report to Real-Life Support in the UK
With your assessment report in your hands, the next move is to get the right professional support. In the UK, this journey almost always starts with your GP, who acts as the main gateway to specialised NHS mental health services.
Booking an appointment to talk through your private assessment is a crucial first step. You'll want to clearly explain your results and give your doctor a sense of how emotional dysregulation impacts your day-to-day life. Having documented evidence from a formal emotional dysregulation test gives your GP the solid information they need to make a well-informed referral.
To get the most out of your appointment, it helps to be prepared.
- Bring Your Report: Have a printed or digital copy of your full diagnostic report ready to share.
- Summarise Your Struggles: Think of a few clear, real-life examples of how your emotional responses affect your job, relationships, or overall wellbeing.
- Ask for a Specific Referral: You can request a referral to a local mental health team that has experience with ADHD, autism, or the specific therapies mentioned in your report.
Finding the Right Therapy for You
Your assessment will most likely point you toward therapies designed to help you build emotional regulation skills. The two most common and effective approaches are Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT) and Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT). Knowing a bit about each one will help you have a more productive conversation with your doctor.
Dialectical Behaviour Therapy (DBT): This was originally created to help people struggling with very intense emotional swings. DBT is fantastic for teaching practical skills across four key areas: mindfulness, tolerating distress, regulating emotions, and navigating relationships. It's especially powerful for anyone who feels their emotions are just too chaotic to manage.
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT): This approach zooms in on identifying and changing unhelpful thought patterns and behaviours. A CBT therapist works with you to spot the triggers for your emotional reactions and helps you develop new, healthier ways of responding. It's a very structured and goal-focused type of therapy.
An assessment result is your most powerful tool for self-advocacy. It provides the language and evidence you need to communicate your needs clearly to healthcare providers, ensuring you are not just heard but also directed toward the support that will make a real difference.
Ultimately, your assessment is the foundation for building a personalised toolkit of coping strategies. It’s what empowers you to shift from simply reacting to your emotions to intentionally managing them. By understanding the "why" behind your feelings, you can finally start building a life that feels less like being caught in a storm and more like a journey you're confidently navigating on your own terms.
Where Do We Go From Here? How Insight Diagnostics Global Can Help
Trying to make sense of your emotional world can be a lonely and confusing journey, especially when you suspect something bigger, like ADHD or autism, might be at play. We get it. That’s why at Insight Diagnostics Global, we’ve built our entire service around a clear, supportive path to understanding your mental health. You don’t have to piece this puzzle together by yourself.
Our whole philosophy is simple: a diagnosis is useless unless it captures the full picture of who you are.
This is exactly why we include a thorough evaluation of emotional dysregulation as a core, non-negotiable part of our comprehensive ADHD and autism assessments. For us, it’s not an optional extra; it’s fundamental to understanding your unique neurotype and the real-world challenges you face every day. We’re here to bring clarity to adults across the UK who are tired of just guessing.
An Expert Process That Puts You First
When you come to us, you're not just a set of symptoms. You'll be working directly with our expert clinical team of GMC-registered consultant psychiatrists. We stick to the gold-standard diagnostic tools and structured clinical interviews because we believe you deserve findings that are solid, dependable, and genuinely useful. The whole experience is designed to be a safe, non-judgmental space where you can finally be heard.
Here’s a quick look at what the process feels like:
- Initial Chat: We start with a proper conversation to hear your story, understand your concerns, and figure out the right assessment path for you.
- The Full Assessment: This involves in-depth online interviews and carefully chosen questionnaires that help us map out your emotional patterns, behaviours, and life history.
- A Clear, Practical Report: You won’t get a report filled with jargon. You’ll receive a clear diagnostic summary that explains what the findings mean for your life. It’s packed with personalised recommendations for what to do next.
At Insight Diagnostics Global, we want to be more than just a clinic; we want to be your trusted partner. Our job is to replace confusion with clarity, giving you the insight you need to get the right support and build a life that actually works for you.
By making an emotional dysregulation test a standard part of our main assessments, we make sure a huge piece of your daily experience isn't ignored. We believe that’s the only way to arrive at a truly accurate diagnosis and create a realistic roadmap for your future.
Frequently Asked Questions
After delving into what an emotional dysregulation test involves, it's completely normal to have a few more questions bubble up. Let's walk through some of the most common ones to give you the clarity you need to decide what to do next.
Can I Self-Diagnose Emotional Dysregulation with an Online Test?
In a word, no. While a quick online quiz can be a useful first step—getting you to think about your emotional patterns and whether you should speak to someone—it’s not a diagnostic tool. Think of it as a signpost, not a destination.
An online screener simply can’t offer the scientific rigour or clinical judgement needed for a real diagnosis. That can only come from a qualified healthcare professional, like a clinical psychologist or psychiatrist, who will carry out a comprehensive evaluation. They’ll look at your entire history, rule out other possibilities, and give you a conclusion you can actually trust.
How Long Does a Formal Emotional Dysregulation Assessment Take?
There isn't a single set timeframe, because assessing emotional dysregulation is rarely done in isolation. It’s almost always part of a much bigger picture, like a full assessment for ADHD or autism. It’s a thorough, multi-stage process, not a one-off appointment.
The journey usually looks something like this:
- An initial chat that lasts about an hour.
- Filling out detailed questionnaires on your own time.
- The main diagnostic interview, which can take anywhere from two to four hours.
Once these are done, the clinician takes time to analyse everything and write up a detailed report. The whole process wraps up with a feedback session where they explain the findings and discuss what comes next.
A professional assessment is designed to be meticulous. The time invested ensures that the final report is not just a label but a useful, personalised guide that truly reflects your experiences and provides clear, actionable recommendations for support.
Are These Assessments Suitable for Children and Teenagers?
Yes, absolutely. The tests and methods used are carefully chosen and adapted for different age groups to make sure they're a good fit. A good clinician will always use age-appropriate tools.
With younger children, for instance, the process leans more on information from parents and teachers through special questionnaires, combined with the clinician's direct observations. For teenagers, it’s more of a mix, often involving their own self-report forms, conversations with parents, and confidential one-on-one sessions with the teen.
This tailored approach is crucial. It helps build an accurate and complete picture of how a young person is managing their emotions, whether that’s linked to potential ADHD, autism, or other mental health challenges. It makes sure the assessment is sensitive, sound, and ultimately leads to the right kind of support at home and at school.
If you are an adult in the UK seeking clarity about your emotional health, particularly in relation to ADHD or autism, Insight Diagnostics Global is here to guide you. Our expert-led, CQC-regulated online assessments provide the clear, definitive answers you need to move forward with confidence. Start your journey towards understanding and support today.








